The Evolution of Gender Roles: A Historical Perspective
Introduction
Gender roles, the societal expectations of behavior based on gender, have evolved significantly over time. This historical perspective examines the shifting roles of gender throughout history, highlighting key changes and their impacts on society. Understanding this evolution provides insight into the current state of gender roles and helps anticipate future developments.
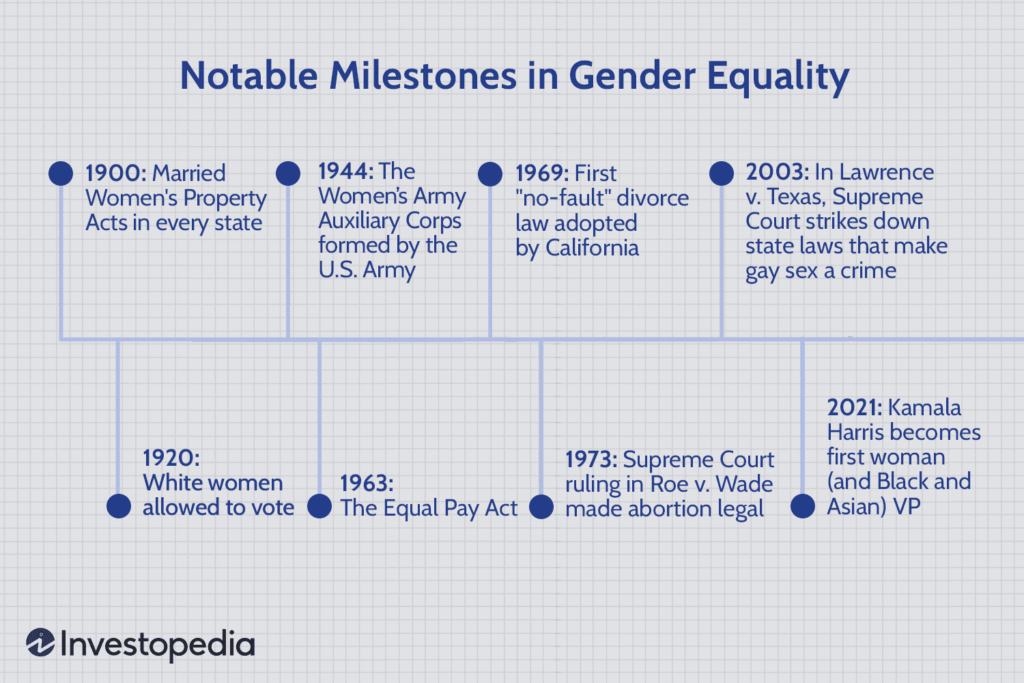
Early Historical Perspectives on Gender Roles
Ancient Societies
In ancient societies, gender roles were often rigidly defined:
- Traditional Roles: Men typically held roles related to warfare, hunting, and governance, while women were often responsible for domestic duties and child-rearing.
- Cultural Norms: These roles were reinforced by cultural and religious norms, shaping societal structures.
Case Example: Ancient Greece and Rome
In ancient Greece and Rome, men dominated public life, including politics and education, while women’s roles were largely confined to the household.
Medieval Period
During the medieval period, gender roles were influenced by feudal systems and religious doctrines:
- Feudal Society: Men primarily engaged in agriculture, military service, and governance, whereas women managed households and assisted in agricultural work.
- Religious Influence: The church reinforced traditional gender roles, with men often holding positions of power and women’s roles limited to domestic spheres.
Case Example: The Role of Women in Medieval Europe
Women in medieval Europe had some economic power through roles in agriculture and commerce but were generally restricted to domestic and supportive roles.
The Renaissance and Enlightenment: Shifts in Gender Roles
Renaissance Era
The Renaissance period began to challenge traditional gender roles:
- Intellectual Pursuits: Increased emphasis on education and intellectual pursuits led to some women engaging in scholarly activities.
- Cultural Change: Women’s roles in art and literature became more prominent, though societal expectations largely remained conservative.
Case Example: Women Artists of the Renaissance
Women like Artemisia Gentileschi began to gain recognition as artists during the Renaissance, challenging traditional gender norms in the arts.
Enlightenment Period
The Enlightenment period brought about significant changes in gender roles:
- Advocacy for Equality: Enlightenment thinkers began advocating for gender equality and the rights of women.
- Educational Opportunities: Increased access to education for women began to challenge traditional gender roles.
Case Example: Mary Wollstonecraft
Mary Wollstonecraft’s writings in the 18th century, such as “A Vindication of the Rights of Woman,” advocated for women’s education and equality, marking a significant shift in gender role perceptions.
The 19th and 20th Centuries: Modernization and Change
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution brought dramatic changes to gender roles:
- Economic Shifts: Women began working in factories and participating in the workforce, challenging traditional domestic roles.
- Social Movements: The period saw the rise of women’s suffrage and labor movements advocating for gender equality.
Case Example: Women’s Suffrage Movement
The women’s suffrage movement in the late 19th and early 20th centuries successfully secured voting rights for women in many countries, marking a significant shift in gender roles.
Post-World War II Era
Post-World War II, gender roles continued to evolve:
- Women in the Workforce: Women’s participation in the workforce increased, driven by economic needs and changing social norms.
- Feminist Movements: The feminist movements of the 1960s and 1970s challenged traditional gender roles and advocated for equal rights.
Case Example: The Second Wave of Feminism
The second wave of feminism, led by figures like Betty Friedan and Gloria Steinem, addressed issues such as workplace discrimination, reproductive rights, and gender equality.
Contemporary Perspectives on Gender Roles
21st Century Developments
In the 21st century, gender roles are increasingly fluid and diverse:
- Increased Representation: There is greater representation of diverse gender identities and expressions in media and public life.
- Changing Norms: Gender roles are increasingly recognized as fluid, with growing acceptance of non-binary and genderqueer identities.
Case Example: Gender Fluidity and Non-Binary Recognition
The recognition and acceptance of non-binary and genderqueer identities reflect ongoing changes in societal understandings of gender roles.
Future Directions
The future of gender roles will likely continue to evolve:
- Inclusive Policies: Advances in gender-inclusive policies and practices are expected to further challenge and reshape traditional roles.
- Cultural Shifts: Ongoing cultural shifts will likely continue to expand the definitions and expectations of gender roles.
Case Example: Gender-Inclusive Legislation
Recent legislative changes, such as gender-neutral options on identification documents, illustrate the ongoing evolution towards more inclusive gender roles.
Conclusion
The evolution of gender roles reflects significant historical, social, and cultural changes. From rigid roles in ancient societies to increasingly fluid and diverse understandings in the modern era, gender roles have continuously adapted. Examining this historical perspective provides valuable insights into current gender dynamics and future developments. As society continues to progress, ongoing efforts to challenge traditional gender norms and promote inclusivity will shape the future of gender roles.



