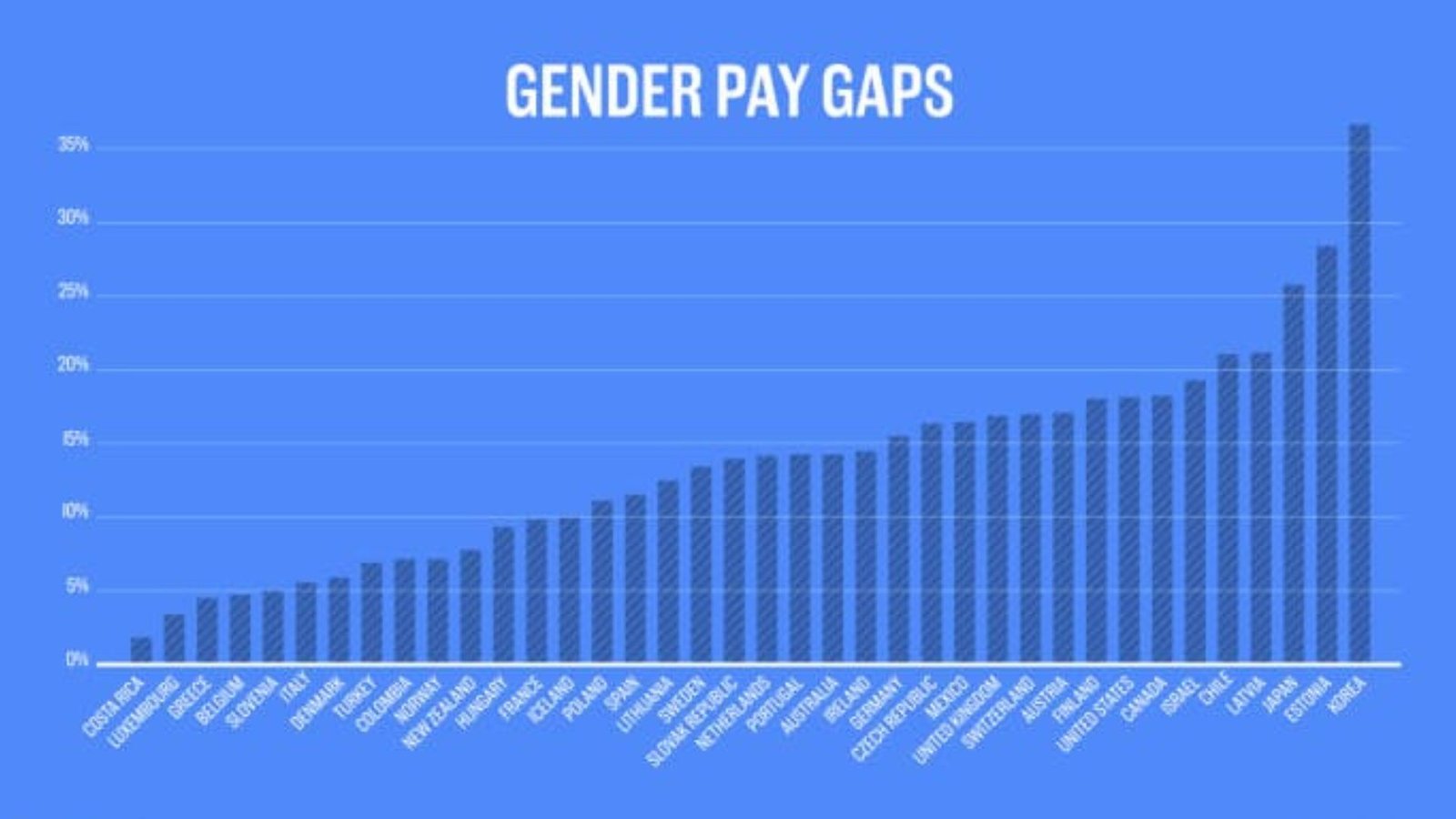
Gender Pay Gap and Economic Impact
The gender pay gap is a significant issue affecting both individuals and economies worldwide. It refers to the difference in earnings between men and women. Understanding the gender pay gap and its economic impact helps highlight why addressing this issue is crucial for creating fair and equitable workplaces.

What is the Gender Pay Gap?
The gender pay gap represents the difference in average earnings between men and women. It is often expressed as a percentage of men’s earnings. For example, if women earn 80 cents for every dollar men earn, the gender pay gap is 20%. This gap can be observed in various industries and occupations, and it reflects broader issues related to gender inequality.
Factors Contributing to the Gender Pay Gap
Several factors contribute to the gender pay gap, including:
- Occupational Segregation: Men and women often work in different fields, with traditionally male-dominated industries typically paying more. For instance, women are more likely to work in lower-paying sectors such as healthcare and education, while men are often in higher-paying fields like technology and engineering.
- Work Experience: Differences in work experience and career interruptions can affect earnings. Women are more likely to take career breaks for caregiving responsibilities, which can impact their long-term earnings and career advancement.
- Education and Skills: Although women have made significant strides in education, they may still face barriers to accessing high-paying positions. For example, women might face challenges in advancing to leadership roles despite having similar qualifications as their male counterparts.
- Discrimination: Gender-based discrimination in hiring, promotion, and pay decisions can contribute to the gender pay gap. Biases and stereotypes can affect how women are perceived and rewarded in the workplace.
Economic Impact of the Gender Pay Gap
The gender pay gap has broad economic implications for individuals and societies:
- Reduced Earnings for Women: Women generally earn less over their careers compared to men. This disparity can lead to lower lifetime earnings and savings, affecting women’s financial security and retirement plans.
- Economic Growth: The gender pay gap can hinder overall economic growth. When women are underpaid or undervalued, their purchasing power is reduced, which can impact consumer spending and economic productivity.
- Increased Poverty Risk: Lower earnings and reduced career advancement opportunities can increase the risk of poverty for women, particularly single mothers and older women. This economic insecurity affects their quality of life and well-being.
- Talent Utilization: The gender pay gap can lead to underutilization of talent. If women are not equally compensated, their potential contributions to the economy and various industries may be limited.
Strategies to Address the Gender Pay Gap
To address the gender pay gap, several strategies can be effective:
- Pay Transparency: Implementing pay transparency policies helps ensure that compensation is fair and equitable. By making salary information available, organizations can identify and address discrepancies in pay.
- Equal Pay for Equal Work: Enforcing laws and regulations that mandate equal pay for equal work is crucial. Organizations should conduct regular pay audits to ensure compliance and address any identified gaps.
- Support for Career Advancement: Providing support for women’s career advancement, such as mentoring, training, and leadership development programs, helps women progress into higher-paying roles and reduce the pay gap.
- Work-Life Balance: Offering flexible work arrangements and supportive policies for caregiving responsibilities can help reduce career interruptions for women. This support allows women to maintain continuous career growth and earnings.
- Addressing Discrimination: Tackling gender-based discrimination through training and awareness programs helps create a fairer work environment. Organizations should work to eliminate biases in hiring, promotion, and pay decisions.
- Encouraging Female Participation: Encouraging women to enter and remain in high-paying fields, such as STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics), can help close the gender pay gap. Providing scholarships and incentives for women in these areas supports greater gender parity in these professions.
The Path Forward
Addressing the gender pay gap requires a concerted effort from governments, businesses, and individuals. By implementing effective strategies and promoting gender equality, we can work towards closing the gap and ensuring fair compensation for all.
Efforts to tackle the gender pay gap not only benefit individuals but also contribute to overall economic growth and societal well-being. Creating equitable workplaces and addressing disparities in pay helps build a more inclusive and prosperous society.
Conclusion
In summary, the gender pay gap is a complex issue with significant economic implications. Factors such as occupational segregation, work experience, and discrimination contribute to the disparity in earnings between men and women. Addressing the gap requires a multifaceted approach, including pay transparency, equal pay laws, and support for career advancement.
By recognizing the economic impact of the gender pay gap and implementing effective strategies, we can work towards achieving pay equality. Ensuring fair compensation for all individuals not only promotes justice but also enhances economic growth and societal prosperity.