The Evolution of Human Rights: From Declaration to Global Movement
The Origins of Human Rights
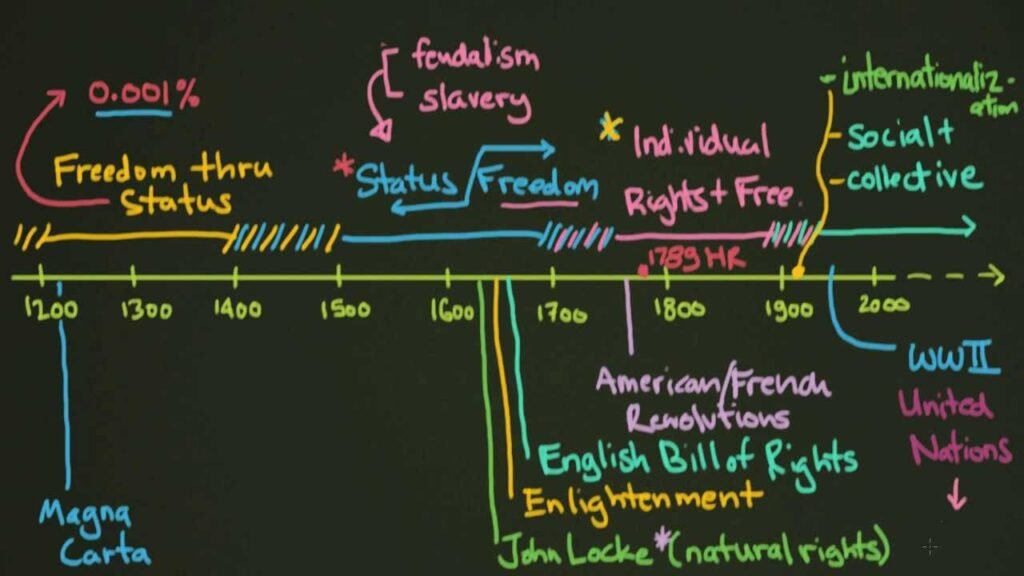
The concept of human rights has evolved significantly over centuries, starting with early philosophical and religious ideas about justice and equality. The modern framework for human rights, however, took shape in the aftermath of World War II. The atrocities of the war highlighted the urgent need for a universal set of principles to protect human dignity and prevent future abuses.
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights
In 1948, the United Nations adopted the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR), a landmark document that set forth fundamental rights and freedoms to which all individuals are entitled. The UDHR, drafted by a diverse committee led by Eleanor Roosevelt, established a common standard for human rights and laid the groundwork for international human rights law. Its core principles emphasize equality, non-discrimination, and the right to life, liberty, and security.
The Growth of Human Rights Institutions
Following the adoption of the UDHR, the global human rights movement gained momentum. The establishment of various international institutions and treaties marked significant milestones in the evolution of human rights. The International Criminal Court (ICC), established in 2002, plays a crucial role in prosecuting individuals for crimes such as genocide and war crimes. The creation of specialized agencies, such as the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR), further supports the promotion and protection of human rights globally.
Expanding Human Rights Frameworks
As the human rights movement evolved, the scope of human rights expanded beyond the initial declarations. International treaties and conventions were developed to address specific issues and groups. Key documents include:
- The Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW): Adopted in 1979, CEDAW focuses on women’s rights and gender equality.
- The Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC): Adopted in 1989, the CRC establishes rights for children, emphasizing protection, education, and participation.
- The Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD): Adopted in 2006, the CRPD promotes the rights and dignity of individuals with disabilities.
These documents reflect a growing recognition of the need to address diverse and evolving human rights issues.
The Role of Non-Governmental Organizations
Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) have played a pivotal role in advancing human rights. Organizations such as Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch have been instrumental in advocating for human rights, documenting abuses, and mobilizing global support. These NGOs often work on the ground, providing aid and raising awareness about human rights violations. Their efforts have contributed to significant changes and improvements in human rights conditions worldwide.
The Impact of Globalization
Globalization has both positively and negatively affected human rights. On one hand, globalization has facilitated the spread of human rights norms and facilitated international cooperation. The internet and global media have increased awareness of human rights issues and enabled rapid mobilization of support. On the other hand, globalization has also led to challenges, such as exploitation and inequality. Addressing these challenges requires a balanced approach that upholds human rights while navigating the complexities of a globalized world.
Emerging Human Rights Issues
As the human rights movement continues to evolve, new issues have emerged. These include:
- Digital Rights: With the rise of technology, issues related to privacy, data protection, and digital freedom have become increasingly prominent.
- Climate Justice: The impact of climate change on vulnerable populations raises concerns about environmental justice and the right to a healthy environment.
- Refugee and Migrant Rights: Conflicts, economic instability, and environmental changes have led to increased migration, highlighting the need for protection and support for refugees and migrants.
Addressing these emerging issues requires innovative approaches and continued advocacy.
The Future of Human Rights
The future of human rights involves building on past achievements while addressing contemporary challenges. Strengthening international cooperation, promoting inclusivity, and adapting to new developments are crucial for advancing human rights. The global community must continue to uphold the principles of the UDHR and work towards a world where human dignity and equality are universally recognized and protected.
Conclusion
The evolution of human rights from the Universal Declaration to a global movement reflects significant progress and ongoing challenges. From the foundational principles established in 1948 to the current focus on emerging issues, the human rights movement has made substantial strides. Continued commitment to human rights is essential for addressing inequalities, protecting vulnerable populations, and ensuring a just and equitable world for all.



